KEEP UP WITH OUR DAILY AND WEEKLY NEWSLETTERS
happening this week! holcim, global leader in innovative and sustainable building solutions, enables greener cities, smarter infrastructure and improving living standards around the world.
PRODUCT LIBRARY
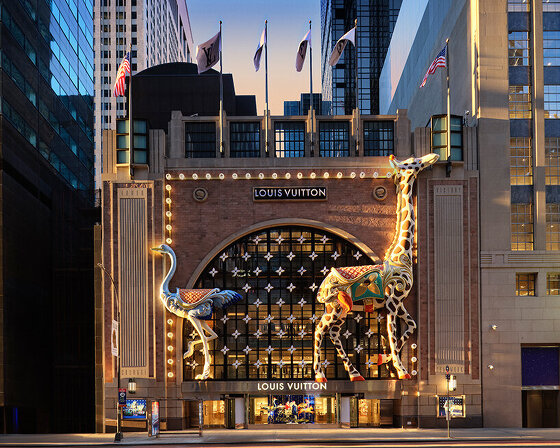
comprising a store, café, and chocolate shop, the 57th street location marks louis vuitton's largest space in the U.S.
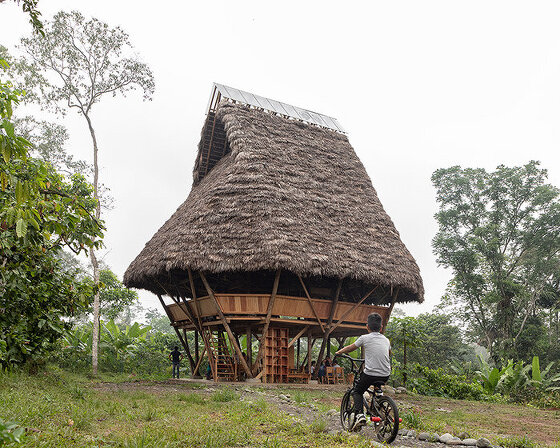
beneath a thatched roof and durable chonta wood, al borde’s 'yuyarina pacha library' brings a new community space to ecuador's amazon.
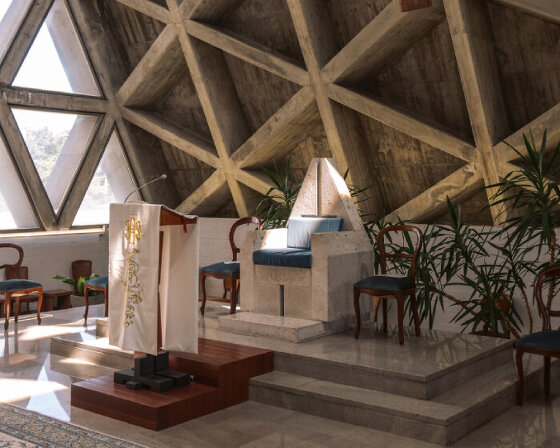
from temples to housing complexes, the photography series documents some of italy’s most remarkable and daring concrete modernist constructions.
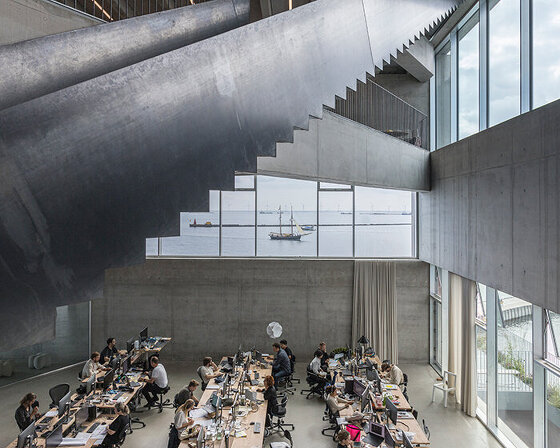
built with 'uni-green' concrete, BIG's headquarters rises seven stories over copenhagen and uses 60% renewable energy.

 hexagonal solar skin
hexagonal solar skin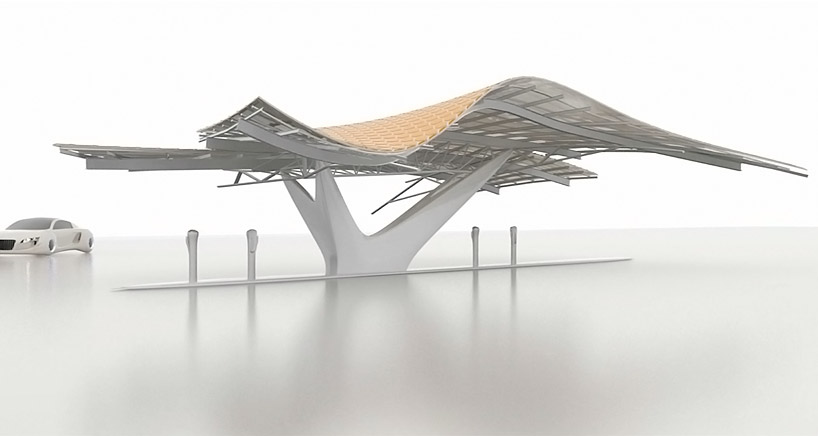 charging station
charging station detail of hexagonal cells
detail of hexagonal cells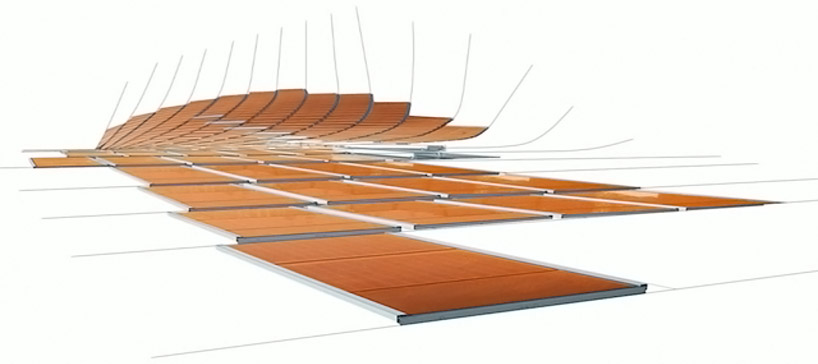 process image of solar powered cells being placed on a wire frame
process image of solar powered cells being placed on a wire frame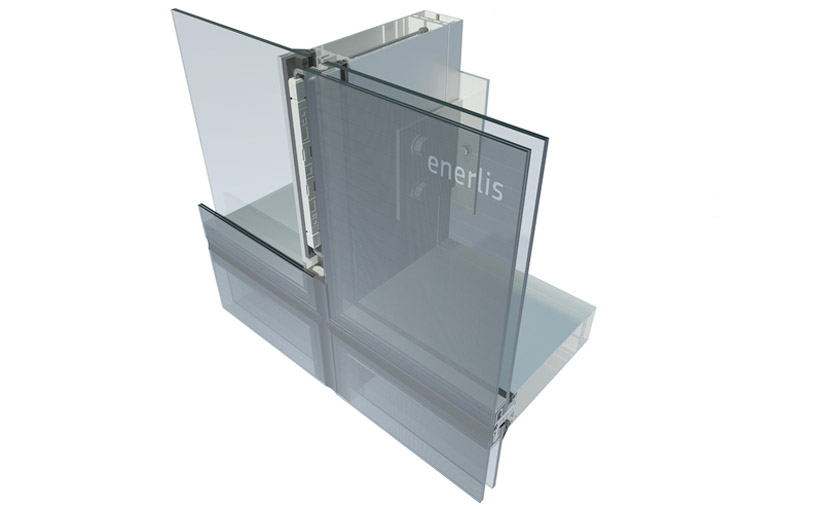 single
single  a section of a solar curtain wall as it is being assembled
a section of a solar curtain wall as it is being assembled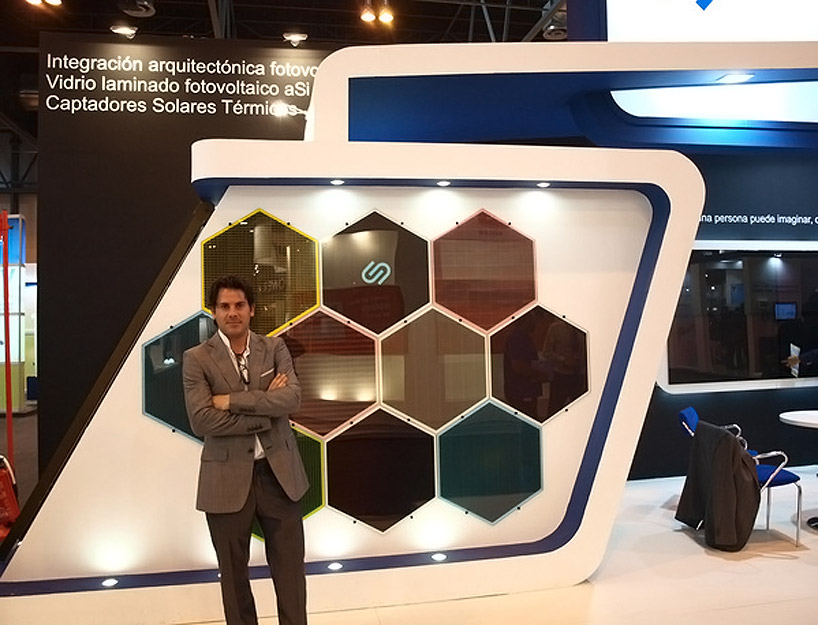  architect martín ferrero by a display showing the variety of colors and pattens in which the glass can be manufactured
architect martín ferrero by a display showing the variety of colors and pattens in which the glass can be manufactured glass produced by
glass produced by 










