
The light of memories by strelitia from romania
designer's own words:
We all want to keep alive in our souls, through memories, the ones that used to be an important part of our world.
Thinking of this, we wanted to make this process more visible and touchable .Through the grieving period we tend to go back to the places, pictures and letters that can bring us closer to the ones we lost, that is why we imagined the cemetery as a place of remembrance, a place that can bring us closer and let us keep alive the memory of those we miss.
Pillars of all sorts (obelisks, columns, etc.)used to be erected in the honor of a victory or of a person, having engraved on it the whole story.
The pillar has a great visual and symbolic value representing the link between heaven and earth. Each pillar holds the story left behind by the ashes of the person resting at the very core of it.
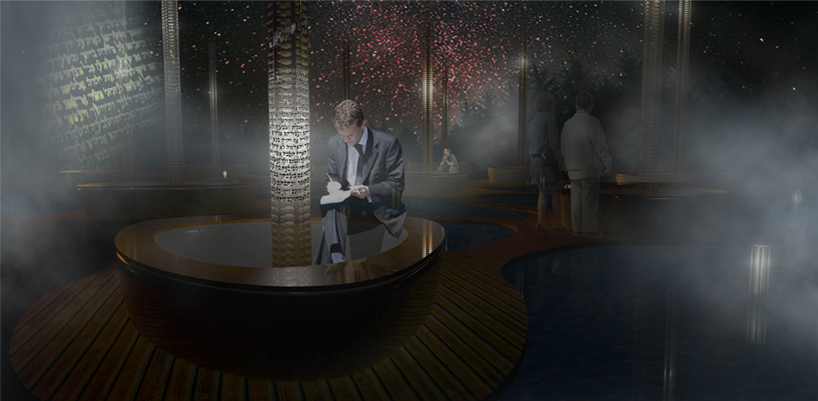
When one comes here to remember all the moments and stories, they are given the opportunity to share the moments as projections on a fog screen.
The beauty of the projections lies in the way they are made real, being generated by the very person who comes there.
Thermoelectricity is electricity produced directly from heat. The production of electricity from heat is called the Seebeck effect, after the German physicist Thomas J. Seebeck, who discovered the phenomenon in the 1820's. Thermoelectricity arises in an electric circuit in which two different conductors (for example, metals) are joined at their ends, and when one of the junctions is at a different temperature than the other, a direct electric current will flow in the circuit. For a given thermoelectric circuit operating in a given temperature range, the magnitude of the current depends mainly on the temperature difference between the two junctions, the greater the temperature difference, the larger the current.
An explanation of the Seebeck effect requires an understanding of the behavior of electrons inside a metal. Not all the electrons inside a metal are bound to specific atoms; some are free to move about. These free electrons behave like a gas. The density of the "free" electrons (the number per unit volume) differs from metal to metal. Consequently, when two different metals are placed in contact, their electron gasesdiffuse into one another. Because of the different densities of the electron gases and because electrons carry an electrical charge, the metals at the junction become oppositely charged. This difference in charge produces a potential difference (voltage like a battery) across the junction. The extent of diffusion of the "electron gases" depends on the temperature. If the two junctions are at different temperatures, a potential difference will exist between the junctions and a current will flow.
Each body releases heat and we capture that heat on the surface they are sitting on. This surface then transfers the heat to a surface cooled by the water. This is the basic transfer for the process of energy generating. This energy is then used to light up the LED cable that projects the photo film negative onto the fog screen.
The light travels through the pillar projecting the story, and after the visitors leave, it fades out and then remains motionless until the process starts again.
close view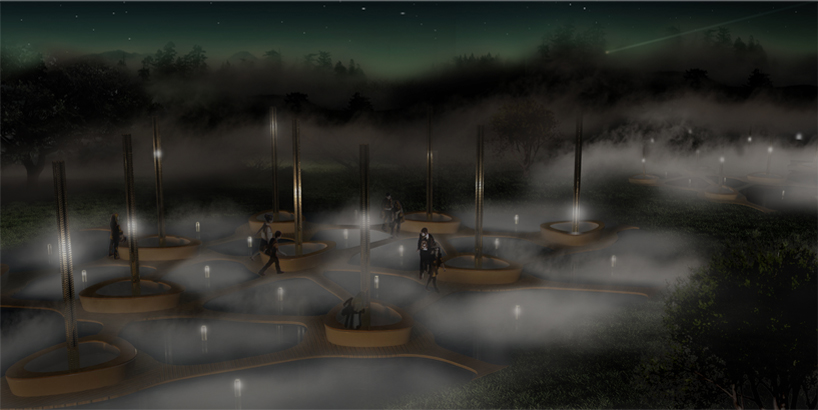
bird eye view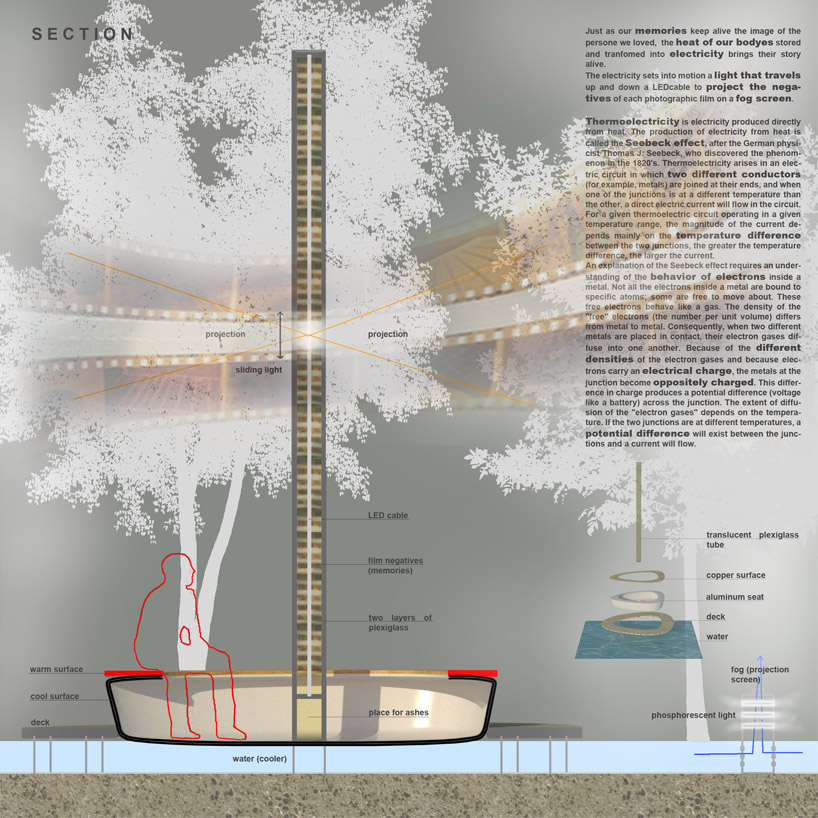
section and technology
hypothetical site plan